Data Structure & Algorithms_ JAVA (Tree)
Wednesday, August 20, 2014
Thursday, July 10, 2014
Connect nodes at same level - Java
Example
Input Tree
A
/ \
B C
/ \ \
D E F
Output Tree
A---> NULL
/ \
B--> C--> NULL
/ \ \
D--> E--> F--> NULL
Method 1 (Extend Level Order Traversal or BFS)
Connect nodes at same level using constant extra space:
Tuesday, July 8, 2014
Friday, July 4, 2014
Wednesday, July 2, 2014
Double Tree
So the tree…
2 / \ 1 3is changed to…
2
/ \
2 3
/ /
1 3
/
1
And the tree 1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
is changed to 1
/ \
1 3
/ /
2 3
/ \
2 5
/ /
4 5
/
4
Program:
Reference:
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/double-tree/
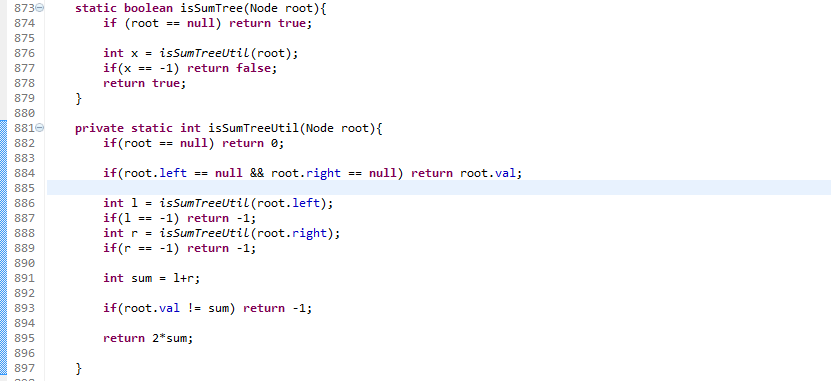
Root to leaf path sum equal to a given number
Idea:
- First check base conditions as per arguments passed in function.
- Take a subsum as a local variable for per stack which substracts the previous node values.
- check if node is leaf and subsum equals to zero then return true.
- if we find above condition true in any call then it has DONE and return true for each calls.
Program:
Tuesday, July 1, 2014
Inorder Tree Traversal without recursion and without stack in java
Using Morris Traversal, we can traverse the tree without using stack and recursion. The idea of Morris Traversal is based on Threaded Binary Tree. In this traversal, we first create links to Inorder successor and print the data using these links, and finally revert the changes to restore original tree.
Program :
Reference:
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/inorder-tree-traversal-without-recursion-and-without-stack/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)